Aktinij
89
Ac
Skupina
n/a
Perioda
7
Blok
f
Protoni
Elektroni
Neutroni
89
89
138
Opća svojstva
Atomski broj
89
Relativna atomska masa
[227]
Maseni broj
227
Kategorija
Aktinoidi
Boja
Srebrna
Radioaktivan
Da
Od grčke riječi aktis, aktinos, snop ili zraka
Kristalna struktura
Kubna plošno centrirana
Povijest
André-Louis Debierne, a French chemist, discovered actinium in 1899.
He separated it from pitchblende residues left by Marie and Pierre Curie after they had extracted radium.
Friedrich Oskar Giesel independently discovered actinium in 1902 as a substance being similar to lanthanum.
He separated it from pitchblende residues left by Marie and Pierre Curie after they had extracted radium.
Friedrich Oskar Giesel independently discovered actinium in 1902 as a substance being similar to lanthanum.
Elektrona po ljusci
2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 9, 2
Elektronska konfiguracija
[Rn] 6d1 7s2
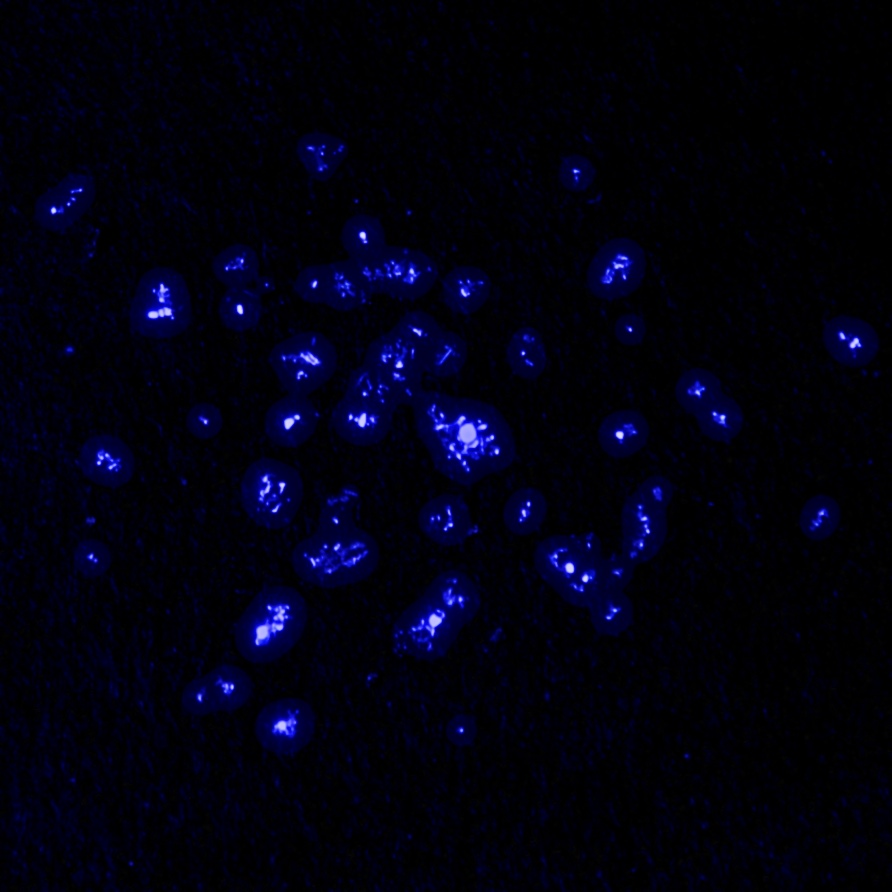
Aktinij svijetli u mraku blijedoplavim svjetlom
Fizikalna svojstva
Agregacijsko stanje
Čvrsto
Gustoća
10,07 g/cm3
Talište
1323,15 K | 1050 °C | 1922 °F
Vrelište
3471,15 K | 3198 °C | 5788,4 °F
Toplina taljenja
14 kJ/mol
Toplina isparavanja
400 kJ/mol
Specifični toplinski kapacitet
0,12 J/g·K
Zastupljenost u Zemljinoj kori
n/a
Zastupljenost u svemiru
n/a
CAS broj
7440-34-8
PubChem CID broj
n/a
Atomska svojstva
Atomski radijus
-
Kovalentni radijus
215 pm
Elektronegativnost
1,1 (Paulingova ljestvica)
Potencijal ionizacije
5,17 eV
Atomski volumen
22,54 cm3/mol
Toplinska vodljivost
0,12 W/cm·K
Stanja oksidacije
3
Primjene
Actinium is used as an active element of radioisotope thermoelectric generators, for example in spacecraft.
The medium half-life of 227Ac makes it very convenient radioactive isotope in modeling the slow vertical mixing of oceanic waters.
225Ac is applied in medicine to produce 213Bi in a reusable generator or can be used alone as an agent for radiation therapy.
The medium half-life of 227Ac makes it very convenient radioactive isotope in modeling the slow vertical mixing of oceanic waters.
225Ac is applied in medicine to produce 213Bi in a reusable generator or can be used alone as an agent for radiation therapy.
Actinium is highly radioactive
Izotopi
Stabilni izotopi
-Nestabilni izotopi
206Ac, 207Ac, 208Ac, 209Ac, 210Ac, 211Ac, 212Ac, 213Ac, 214Ac, 215Ac, 216Ac, 217Ac, 218Ac, 219Ac, 220Ac, 221Ac, 222Ac, 223Ac, 224Ac, 225Ac, 226Ac, 227Ac, 228Ac, 229Ac, 230Ac, 231Ac, 232Ac, 233Ac, 234Ac, 235Ac, 236Ac